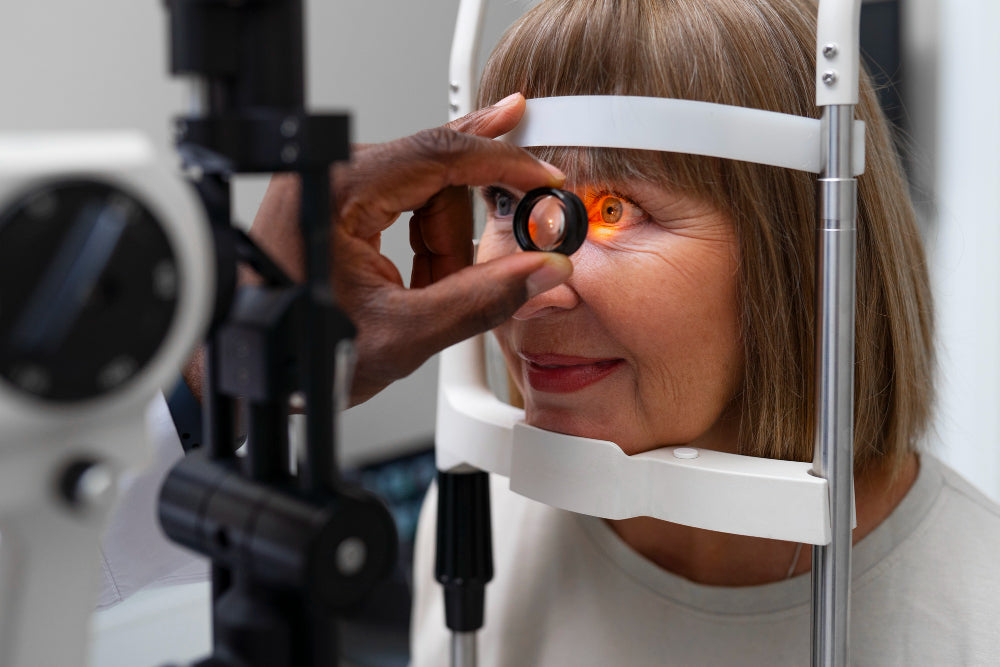
Regular comprehensive eye exams are crucial for optimal eye health. Optomap retinal imaging and pupil dilation are two standard methods used by eye doctors to examine the health of the back of the eye called the retina.
When considering Optomap vs Dilation, here’s the bottom line:
Optomap offers a quick, wide-angle enhanced digital image of the retina without discomfort for most patients.
That being said, dilation may be necessary to enhance Optomap imaging, as for patients with high prescriptions, history of retinal disease, cataracts, patients over the age of 60, and patients with diabetes.
Optomap is always best, but may need to be enhanced with dilation.
Optomap Imaging

Optomap is a noninvasive, ultra-widefield digital imaging technology. It utilizes an elliptical mirror that spins in hydrogen to capture a high-resolution retinal image that captures 270 degrees of the inside of the eye through an undilated pupil (for most people) in one panoramic picture.
This technology allows eye doctors to detect and monitor eye conditions such as glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment and macular degeneration in their early stages. It also assists eye doctors in early detection of systemic disease, such as cancer, multiple sclerosis, diabetes, and hypertension, just to name a few.
Advantages of Optomap over Dilation Alone
- Comfort and Convenience: A significant advantage of Optomap is its comfort and convenience. Optomap is quick and painless. The procedure takes only a few seconds, making it ideal for patients who do not require dilation due to age, prescription, or history of retinal disease.
- No Recovery Time: Since Optomap does not involve dilating the pupils, there is no need for recovery time. Patients immediately return to their daily activities, including computer use and driving.
- Comprehensive View: Optomap provides a detailed and comprehensive retinal view. It helps detect eye and systemic health conditions that would ordinarily go unnoticed through an undilated pupil. Optomap takes a 270 degree wide-field image in seconds and lays it out neatly on the computer screen for you to review with your doctor. This means you can see what your doctor sees inside your eye.
- Record Keeping: The digital images can be stored and compared over time, helping your doctor track changes in the retina and manage long-term eye and systemic health.
- Early Detection of Disease: With Optomap retinal imaging, different layers of the retina can be separated out and viewed to help your doctor identify pathology early on. Early detection leads to better treatment outcomes.
Pros and Cons of Optomap
The potential benefits of Optomap are given above, but to explain it better, we also give you some pros and cons here, in a nutshell.
The Optomap offers a quick, painless way to capture a wide view of the retina without dilating the eyes, making it more convenient for patients. It provides high-resolution images that can help detect eye diseases early.
However, it may miss some peripheral retinal issues and can be more expensive than traditional dilation. Despite these limitations, its efficiency and patient comfort make it a valuable tool in eye care.
Eye or Pupillary Dilation

Pupillary dilation is an older method used by eye doctors to examine the retina. It involves eye drops that temporarily enlarge the pupils, allowing the doctor to see more of the retina and optic nerve.
However, without Optomap retinal imaging, this is still the equivalent of trying to see inside a room looking through a keyhole. (Also, the traditional instruments used to view inside the eye even though a dilated pupil still provide an image that is upside down and backwards! Imagine trying to put that image together in your head!) The Optomap is more the equivalent of opening the door and stepping inside the room to look around.
Sometimes pupillary dilation is still necessary even when coupled with Optomap. Let’s look at these conditions to explore why:
- Patients over the age of 60: As we age, our pupils just naturally get smaller as our autonomic nervous system shifts from the sympathetic fight or flight neural tonus to the parasympathetic rest and digest end of the spectrum. Thus dilation prior to Optomap not only aids in better retinal imaging, but allows your eye doctor to do a more thorough evaluation for cataracts.
- Diabetes: Dilation with diabetes allows for better imaging and earlier detection of microscopic swelling and bleeding of the retina associated with neovascularization. This occurs when tiny new unhealthy blood vessels grow that leak and bleed fluid into the eye, reducing vision and sometimes causing glaucoma.
- Retinal Disease: Patients with a history of retinal detachment, macular degeneration, flashes and floaters, cataracts, and glaucoma can have enhanced retinal imaging with Optomap and dilation allowing for early detection of changes in their condition. These might warrant quicker or different treatment options. This early detection can help prolong normal vision for these patients for years to come.
- High Prescriptions: Patients with high prescriptions are at greater risk for retinal disease. Dilation plus Optomap can detect retinal holes and tears sooner, helping to protect and preserve vision for these high-risk individuals.
Pros and Cons of Eye Dilation
Eye dilation allows doctors to thoroughly examine the retina and detect potential issues, enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Even so, it can cause temporary light sensitivity and blurred vision, making daily tasks challenging for a few hours. Despite the discomfort, it's a crucial procedure for maintaining long-term eye health. Ultimately, the benefits of early detection outweigh the short-term inconveniences.
Optomap Alone Vs. Optomap with Dilation?

Optomap vs. dilation: Which is better?
Your doctor will decide and advise you appropriately. Ask your doctor to review their rationale and they will be happy to do so.
Does Optomap Replace Dilation?

For a majority of patients, the answer is yes. But if you fall into one of the categories listed above, you may require dilation along with Optomap retinal imaging.
Also, your doctor may see something suspicious on your screening Optomap and recommend dilation to further explore the finding. Be sure to follow up here if this is recommended for you. Your eye and overall health could depend on it!
In addition, children ages 10 and younger and those showing signs of accommodative spasm require dilation not to see inside the eye, but to relax the muscles of accommodation. These muscles of focusing can cause the eye to “over-focus” resulting in a patient appearing more nearsighted or less farsighted than they truly are. In this case, stronger eye drops are required to relax these focusing muscles so an accurate measurement of the prescription can be obtained.
What is the Time Required to Get Results from an Optomap Exam?
The Optomap retinal exam is quick and convenient. It captures the retinal image in just seconds. The image will then be transferred to your medical records for you to review with your doctor during the course of your exam.
The Bottom Line
Optomap and dilation aren't rivals; they're teammates!
Optomap captures a wide retinal image quickly and comfortably, but some areas require a closer look. Dilation provides a more detailed view. Today’s dilating drops are quicker acting and don’t last as long as drops in years past. This minimizes the light sensitivity and reduced focusing ability associated with older versions of dilating drops. The office will have dilation sunglasses for you as well. If you have questions about how dilation will affect you, be sure to ask your doctor.
The best approach quite literally depends on you!
Your eye doctor will prescribe the most suitable option for you based on your eye and vision health and systemic health history.
Remember, regular eye exams, including Optomap retinal imaging with or without dilation are critical for catching eye problems early and keeping your vision sharp and healthy for years to come.
Also Read: